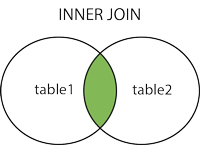
SQL Join is used to combine rows from two or more tables.
Join is based on a common field between the tables.
Northwind Database has table Orders and table Customers.
Orders table can be joined to the Customers table with column CustomerID (Foreign key).
So, if we would like to know the name of the company behind each order we could write:
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CompanyName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Customers
INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.OrderID
ORDER BY Customers.CompanyName; SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;or:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;PS! INNER JOIN is the same as JOIN.

Returns ALL rows from left table with MATCHING rows in right table.
Returns NULL for the right side when there is no match.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;or:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;PS! In some databases LEFT JOIN is called LEFT OUTER JOIN.
-- Get all customers and their orders.
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CompanyName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Customers
LEFT OUTER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CompanyName;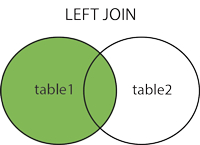
Returns ALL rows from right table with MATCHING rows in left table.
Returns NULL for the left side when there is no match.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;or:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;PS! In some databases RIGHT JOIN is called RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
-- Get all orders and the relevant customers.
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CompanyName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
RIGHT OUTER JOIN Customers ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CompanyName;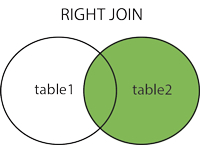
Returns ALL rows from left side and ALL from right side.
Combines the results of both LEFT and RIGHT joins.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;-- Get all orders and all customers, combined.
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CompanyName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
FULL OUTER JOIN Customers ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.OrderID
ORDER BY Customers.CompanyName;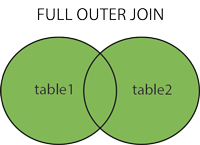
Used in conjuction with aggregate functions to group the result set by one or more columns
Syntax:
One grouped column
SELECT column_name, aggregate_function(column_name2)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator value
GROUP BY column_name;More than one grouped columns
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, aggregate_function(column_name3)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name1, column_name2;-- How many orders has each customer from UK placed?
SELECT Customers.CompanyName, COUNT(Orders.OrderID)
FROM Customers
LEFT JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
WHERE Customers.Country = 'UK'
GROUP BY Customers.CompanyName;-- How many objects has each customer from UK ordered each year?
SELECT Customers.CompanyName, YEAR(Orders.OrderDate), SUM( [Order Details].Quantity )
FROM Customers
INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
INNER JOIN [Order Details] ON Orders.OrderID = [Order Details].OrderID
WHERE Customers.Country = 'UK'
GROUP BY Customers.CompanyName, YEAR(Orders.OrderDate)
ORDER BY Customers.CompanyName, YEAR(Orders.OrderDate);Used to temporarily rename a table or column heading
SELECT column_name AS alias_name
FROM table_name;SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name AS alias_name;How many objects has each customer from UK ordered each year and how much did the pay?
SELECT C.CompanyName AS [Company Name],
YEAR(O.OrderDate) AS [Year of Order],
SUM( OD.Quantity ) AS [Total Quantity],
SUM( OD.Quantity * OD.UnitPrice * (1-OD.Discount)) AS [Total Revenues]
FROM Customers AS C
INNER JOIN Orders AS O ON C.CustomerID = O.CustomerID
INNER JOIN [Order Details] AS OD ON O.OrderID = OD.OrderID
WHERE C.Country = 'UK'
GROUP BY C.CompanyName, YEAR(O.OrderDate)
ORDER BY C.CompanyName, YEAR(O.OrderDate);Used to insert new records in a table
Syntax:
Insert with values for ALL columns
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES (value1,value2,value3,...);or
Insert with values only for specified columns
INSERT INTO table_name (column1,column2,column3,...)
VALUES (value1,value2,value3,...);INSERT INTO Suppliers(CompanyName, ContactName, Address, City, PostalCode, Country)
VALUES ('Cardinal','Tom B. Erichsen','Skagen 21','Stavanger','4006','Norway'); Deletes one or more rows from a table
Syntax:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE some_column=some_value; Attention: If no WHERE clause is specified, ALL records will be deleted!
-- Deletes from table Suppliers all records with CompanyName = 'Cardinal'
DELETE FROM Suppliers
WHERE CompanyName = 'Cardinal'; Updates existing records
Syntax:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1=value1,column2=value2,...
WHERE some_column=some_value;Attention: If no WHERE clause is specified, ALL records will be updated!
-- Updates the phone with new value for all companies named 'Cardinal'
UPDATE Suppliers
SET Phone = '(0)2-953010'
WHERE CompanyName = 'Cardinal'Sequence of operations performed as a single logical unit of work
You can rollback a transaction and revert changes to the database or commit then.
Syntax Example:
--Update all Customers' Country to Greece and then revert changes
BEGIN TRANSACTION
update customers
set Country = 'Greece';
select Country, *
from Customers;
ROLLBACK
select Country, *
from Customers;