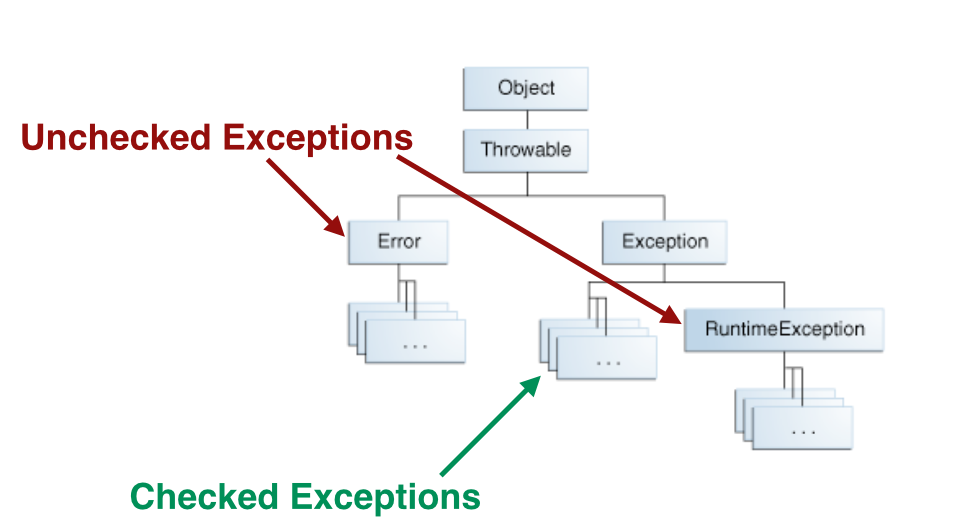
We can use the try-catch construct.
try {
some code here
} catch and finally blocks …We can declare a might-thrown exception in method signatures.
public void writeList() throws IOException, IndexOutOfBoundsException {...}throw new keyword.Then, we need to also declare the exception in the method signature (using throws).
if (ammount < 0) {
throw new NegativeAmmountException();
}
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class testClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
File file = new File("E://file.txt");
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} import java.io.*;
public calss ExcepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int a[] = new int[2];
System.out.println("Access elements three:" + a[3]);
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" +e);
}
System.out.println("Out of the block");
}
}public class ExcepTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = new int[2];
try {
System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}finally {
a[0] = 6;
System.out.println("First element value: " + a[0]);
System.out.println("The finally statement is executed");
}
}
}printStackTrace() to get a stack traceHighLevelException: MidLevelException: LowLevelException
at Junk.a(Junk.java:13)
at Junk.main(Junk.java:4)
Caused by: MidLevelException: LowLevelException
at Junk.c(Junk.java:23)
at Junk.b(Junk.java:17)
at Junk.a(Junk.java:11)
... 1 more
Caused by: LowLevelException
at Junk.e(Junk.java:30)
at Junk.d(Junk.java:27)
at Junk.c(Junk.java:21)
... 3 moreException, RuntimeException.