Array examples:
double[] array = new double[10];
char[] word = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
int[][] 2darray = new int[3][3];You can concatenate strings by using the + operator
String word = "Hello bootcamp!";
word = word + " Winter is coming...";
System.out.println(word);Results to:
Hello bootcamp! Winter is coming...Code example:
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("Hello").append(" StringBuffer!");
System.out.println(sb.toString());Code example:
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Hello").append(" StringBuilder!");
System.out.println(sb.toString());1 to N with the three different ways presented in the previous slides/* Simple String example */
String s = "";
int N = 100000;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
s += String.valueOf(i);
}
/* StringBuilder example */
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
builder.append(i);
}
s = builder.toString();
/* StringBuffer example */
StringBuffer buff = new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
buff.append(i);
}
s = buff.toString();Measuring the separate execution of each solution above resulted to:
* 78.5 millisecond using the += operand
* 3.7 millisecond using StringBuffer
* 1.4 millisecond using StringBuilder// our test String phrase
String message = "Winter is coming...";
// transform a String to a char[] and print it
char[] charArray = message.toCharArray();
for(int i=0; i<charArray.length; i++)
System.out.print(charArray[i] + ", ");
// getting the first word of the phrase
String firstWord = message.substring(0, message.indexOf(' '));
System.out.println("First word: " + firstWord);
// checking if our phrase contains the String "sun"
boolean match = message.contains("sun");
System.out.println("Contains 'sun': " + match);
// getting the last word of the phrase
String lastWord = message.substring(message.lastIndexOf(' ') + 1, message.length());
System.out.println("Last word: " + lastWord);The output of the aforementioned 4 prints is the following:
[W, i, n, t, e, r, , i, s, , c, o, m, i, n, g, ., ., .]
First word: Winter
Contains 'sun': false
Last word: coming...Use ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) in case of initially adding many elements and you want to avoid the incremental size increase
// class declaration according to Oracle
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, .... {
// ...
}import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList declaration and initialization
ArrayList<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<>();
// add elements at the end of the list
myList.add(1);
myList.add(2);
myList.add(4);
System.out.println(myList);
// add an element in a specific position
myList.add(2, 3);
System.out.println(myList);
// check if the list contains a number
System.out.println("List contains 2? " + myList.contains(2) + "\n"
+ "List contains 0? " + myList.contains(0));
// ensures that the internal array will have 1000 elements capacity
myList.ensureCapacity(1000);
// remove all elements from the list
myList.clear();
System.out.println(myList);
}
}with output
[1, 2, 4]
[1, 2, 3, 4]
List contains 2? true
List contains 0? false
[]The entry point into a linked list is called the head of the list
// class declaration according to Oracle
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Queue<E>, .... {
// ...
}class Circle {
/* Linked-list nodes should have a reference of their own
type showing the next element in the list */
private Circle next;
Circle(){ this.next = null; }
public void setNext (Circle c) { this.next = c; }
public Circle getNext () { return this.next; }
/*
* Here follows the code of the original Circle class
* as presented in the Creating Classes session
*/
}
public class CircleList {
private Circle first_element;
CircleList() { this.first_element = null; }
public void addElement(Circle c) {
if(this.first_element == null) {
this.first_element = c;
} else {
Circle current_circle = this.first_element;
while (current_circle.getNext() != null) {
current_circle = current_circle.getNext();
}
current_circle.setNext(c);
}
}
}Deque provides similar but enriched functionality
// The Stack class, as defined by Oracle
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> implements List<E>, ... {
// ...
}import java.util.Stack;
public class StackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Stack declarations and initialization
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// add elements at the top of the stack
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack);
// check the first element
int top = stack.peek();
System.out.println("top element: " + top);
// remove and hold the first element
int first = stack.pop();
System.out.println("popped element: " + first + "\n" + stack);
// check the first element
top = stack.peek();
System.out.println("top element: " + top);
}
}Older additions will be served first
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> { ... }Collections that are not synchronised can be now wrapped in another synchronised object or by applying the following:
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));CaesarsCipher is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet link.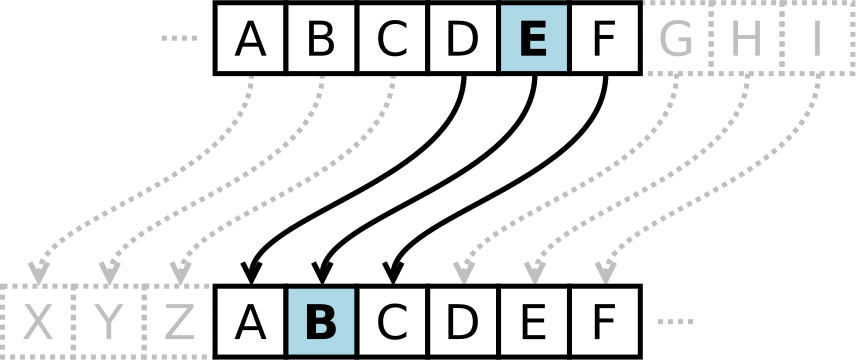
public class ReverseStack {
public static Stack<Integer> reverse(Stack<Integer> initial) {
// fill-in your code here
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> myStack = new Stack<>();
myStack.addAll(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}));
System.out.println("initial stack: " + myStack);
System.out.println("reversed stack: " + reverse(myStack));
}
}The output is
initial stack: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
reversed stack: [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]Create a TestLibrary class and a main method in the class. In the main method execute the following code:
public static void main(String args[]) {
/** Create Random authors */
Author ruth = new Author("Ruth");
Author diane = new Author("Diane");
Author jacqueline = new Author("Jacqueline");
Author rachel = new Author("Rachel");
Author joan = new Author("Joan");
Author theresa = new Author("Theresa");
Author angela = new Author("Angela");
Author helen = new Author("Helen");
Author lisa = new Author("Lisa");
/** Create books with from the existing authors */
Book book1 = new Book("Book1",new Author[]{ruth, joan},"368777540-2",10,2,20);
Book book2 = new Book("Book2",new Author[]{ruth},"963099898-2",10,1,22);
Book book3 = new Book("Book3",new Author[]{jacqueline, rachel},"005382097-2",10,0,23);
Book book4 = new Book("Book4",new Author[]{theresa, angela},"538310208-2",10,3,24);
Book book5 = new Book("Book5",new Author[]{lisa},"562448132-2",10,4,26);
Book book6 = new Book("Book6",new Author[]{helen},"670364563-2",10,2,21);
Book book7 = new Book("Book7",new Author[]{diane, jacqueline},"466916869-2",10,5,17);
Book book8 = new Book("Book8",new Author[]{angela, rachel},"764674973-2",10,0,15);
Book book9 = new Book("Book9",new Author[]{theresa, jacqueline},"052469721-2",10,6,17);
Book book10 = new Book("Book10",new Author[]{angela},"609291817-2",10,3,13);
Book book11 = new Book("Book11",new Author[]{lisa, ruth},"451378028-2",10,8,12);
Book book12 = new Book("Book12",new Author[]{theresa},"142352773-2",10,6,20);
Book book13 = new Book("Book13",new Author[]{lisa, rachel},"115135166-2",10,0,20);
Book book14 = new Book("Book14",new Author[]{helen},"631942468-2",10,3,20);
Book book15 = new Book("Book15",new Author[]{angela, helen},"323662444-2",10,0,23);
Book book16 = new Book("Book16",new Author[]{rachel},"121360492-2",10,0,12);
Book book17 = new Book("Book17",new Author[]{theresa, jacqueline, angela},"391199302-2",10,0,20);
Book book18 = new Book("Book18",new Author[]{angela,lisa},"549307784-2",10,1,20);
Book book19 = new Book("Book19",new Author[]{theresa, helen},"368777230-2",10,23,20);
Book book20 = new Book("Book20",new Author[]{ruth},"793027213-2",10,0,20);
/** Create the BookList from the books array above **/
BookList books = new BookList( new Book[]{book1,book2,book3,book4,book5,book6,book7,
book8,book9,book10,book11,book12,book13,book14,book15,
book16,book17,book18,book19,book20} );
/** Assign the book collection to the library */
Library library = new Library(books);
/* A librarian undertakes the operation of the library */
Librarian librarian = new Librarian(library);
librarian.findMeAvailableBooks();
librarian.findMeBook("Book3");
librarian.findMeBooksFromAuthor("Ruth");
librarian.findMostPopularBook();
// Not existing cases
librarian.findMeBook("Book0");
librarian.findMeBooksFromAuthor("angor");
// Make some transactions
librarian.rentPhysicalCopy("Book1");
librarian.rentPhysicalCopy("Book2");
librarian.rentPhysicalCopy("Book2"); // no available copies left
// execute transactions
librarian.executePendingTransactions();
librarian.executePendingTransactions(); // no pending trans left
// print transactions history
librarian.printTransactionHistory();
// Show menu options
librarian.showOptions();
}Create a method findMinAndPositions that finds the min value of a given array of Integers and also prints its positions.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1, 3, 1, 2, 5, 6, 6, 8, 9, 12, 1, 13, 3, 1};
findMinAndPositions(array);
}The results should be similar to the following:
Min is 1 in positions: 0, 2, 10, 13Can you use only one for loop for solving the exercise?
