Coding Bootcamp: The life of a "Like"
Transistors and gates
- Transistor: a miniature switch
- Logic gate: digital building block
A NAND gate as transistors

By JustinForce - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0
Digits and counting
- Counting with 0 and 1
- How to add two bits
- How to add three bits
- How to add 64 bits with 64 bits
A half adder

A full adder

A four bit adder
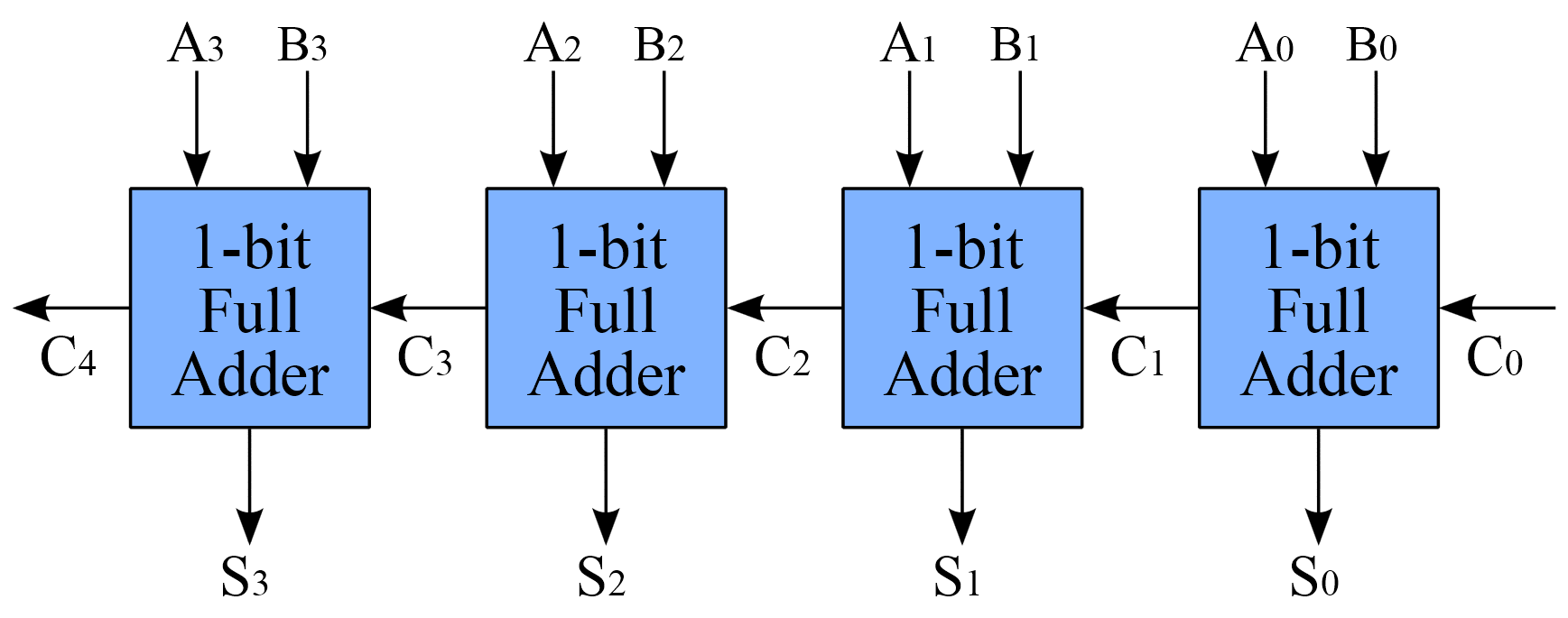
By Cburnett - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0
A four bit ALU

By Poil - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0
- 0000: 0
- 0001: 1
- 0010: 2
- 0011: 3
- 0100: 4
- 0101: 5
- 0110: 6
- 0111: 7
- 1111: -1
- 1110: -2
- 1101: -3
- 1100: -4
- 1011: -5
- 1010: -6
- 1001: -7
- 1000: -8
- 00100001: !
- 00111111: ?
- 00110000: 0
- 00111001: 9
- 01000001: A
- 01000010: B
- 01011010: Z
- 01100001: a
- 01100011: b
- 01111010: z
- 1: 0 01111111 [1]00000000000000000000000
- 1 × 1 × 2127 - 127
- 2: 0 10000000 [1]00000000000000000000000
- 1 × 1 × 2128 - 127
- 3: 0 10000000 [1]10000000000000000000000
- 1 × 1.5 × 2128 - 127
- -1: 1 01111111 [1]00000000000000000000000
- -1 × 1 × 2127 - 127
- 1.5: 0 01111111 [1]10000000000000000000000
- 1 × 1.5 × 2127 - 127
- 1.1: 0 01111111 [1]00011001100110011001101
- 1 × 1.100000023841858 × 2127 - 127
- 1.10000002384185791015625
- 2 × 1030: 0 11100011 10010011111001011001010
- 1 × 1.5777218341827393 × 2227 - 127
- 2000000030094932439753377710080
Ranges
- Integers
- 8-bit (byte): -128 to 127 or 0 to 255
- 16-bit (short): -32768 to 32767 or 0 to 65535
- 32-bit (int): ± 2 bn or 0 to 4 bn
- 64-bit (long): ± 1019
- Floating point numbers
- 32-bit (float/Single): ± 1.2 × 10-38 to ± 3.4 × 1038
- (6 decimal digits)
- 64-bit (double/Double): ± 2.2 × 10-308 to ± 1.8 × 10308
- (15 decimal digits)
Chips and chip construction
- Gates are put together in integrated circuits
- Chips can serve various functions, such as CPU, memory, or interface
- Early ICs contained 2-6 gates (8-30 transistors)
- A modern CPU can contain 20 billion transistors
A NAND gate in CMOS
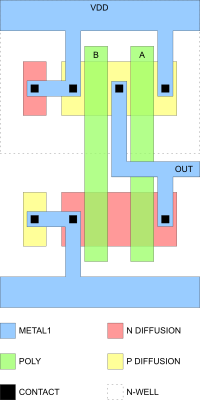
By Jamesm76 at English Wikipedia, Public Domain
Structure of a chip
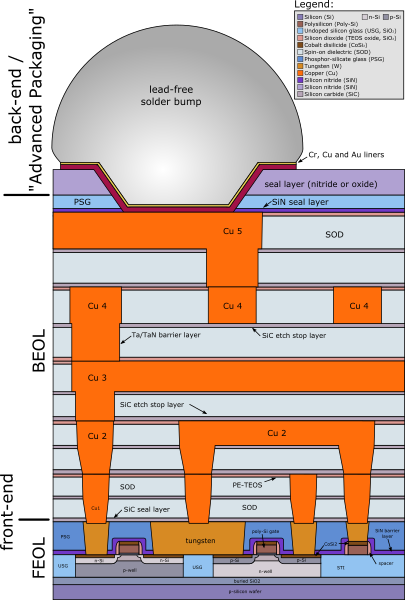
By Cepheiden - self made, CC BY 2.5
A gate in three dimensions

By David Carron at English Wikipedia, Public Domain
A chip in a DIL package
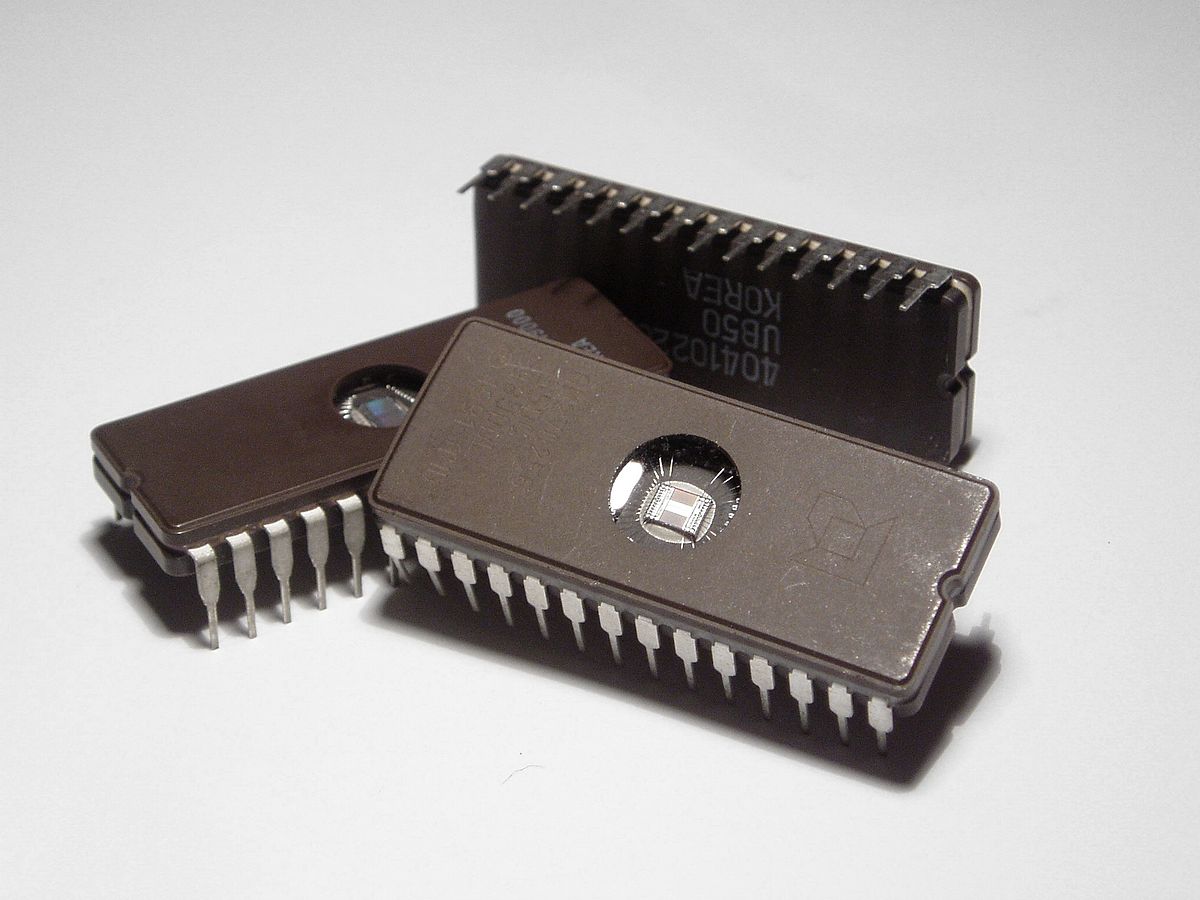
By Zephyris at English Wikipedia - CC BY-SA 3.0
A peek through the window
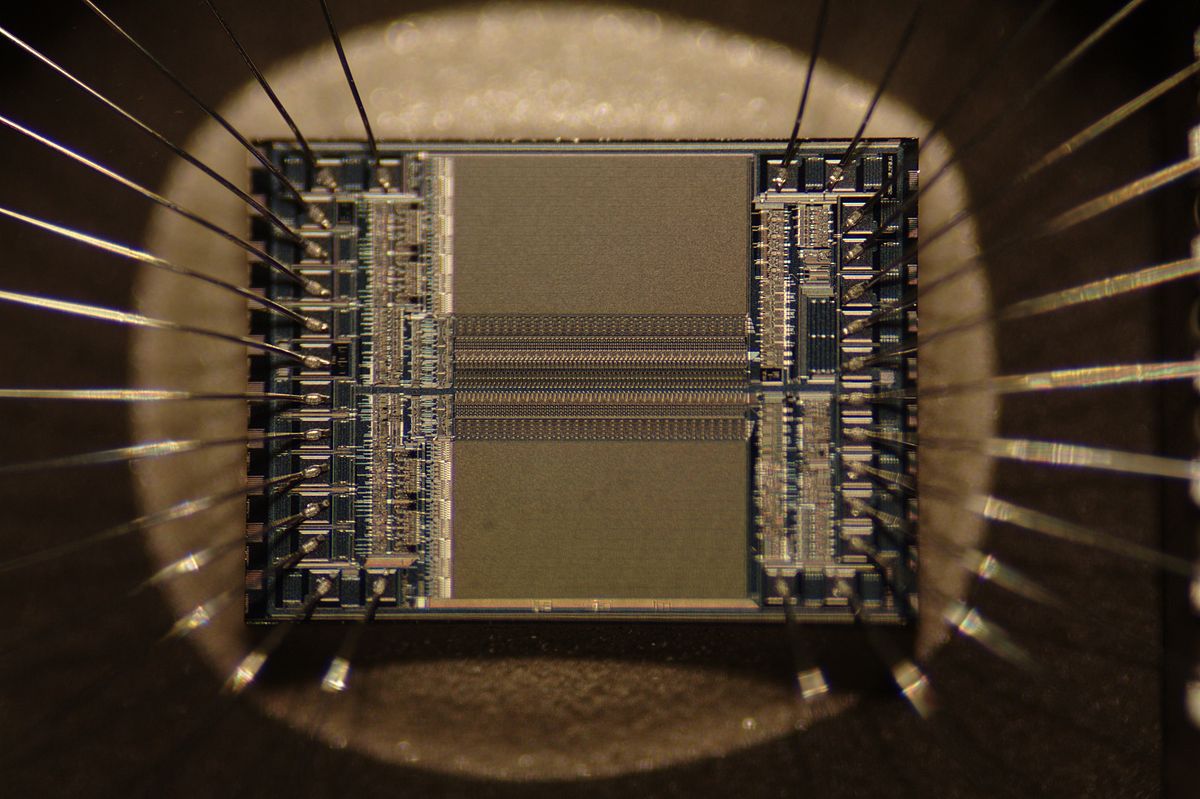
By Zephyris at English Wikipedia - CC BY-SA 3.0
Flash memory through electron microscopy

By Micron Technology Inc.
Inside a modern computer
- CPU
- RAM
- Secondary storage (magnetic disk, SSD)
- ROM
- Interfaces
- USB
- DMA
- Networking
- Graphics
Low-level programming
- Registers
- Arithmetic instructions
- Control flow
- Memory access
- Stack
High-level programming
- Compiling expressions into instructions
- Interpreting instructions
- Tokens
- Constants
- Operators
- Reserved words
- Comments
- Syntax
Commonly used programming languages
- C
- C++, Go, Rust
- Java, C#, Swift
- JavaScript, PHP
- Python, Ruby, Perl
Memory organization
- Code
- Stack
- Heap
- Constants
Operating system
- Process isolation
- Device virtualization
- Multitasking
- Application host
- System calls (API)
Network layers
- Application
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport
- Network
- Link
- Physical
Building the web
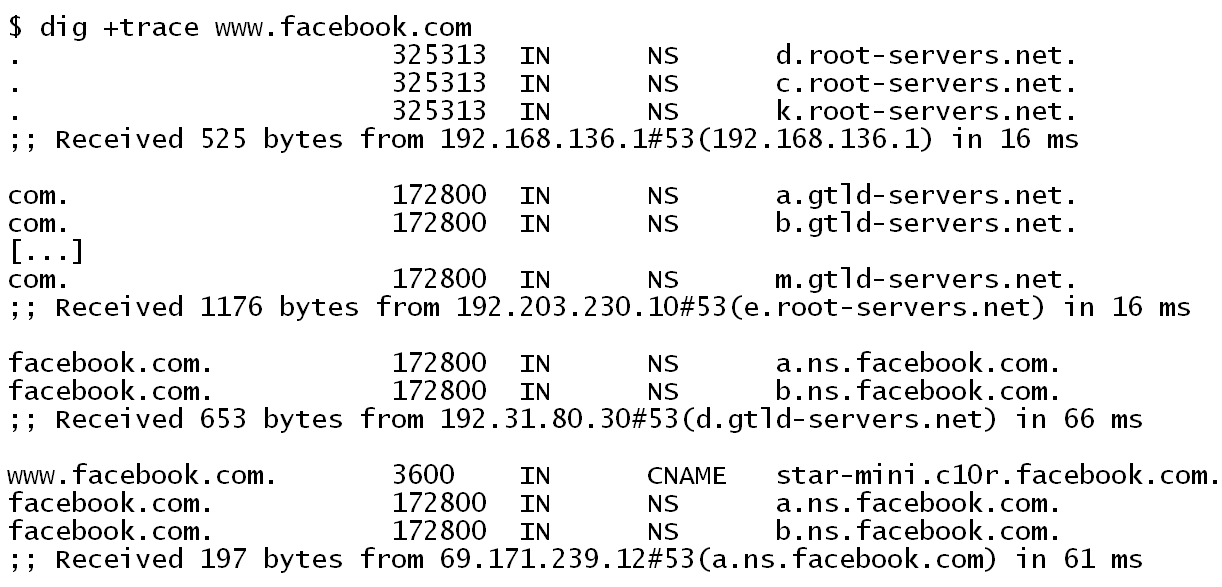
Trace of a DNS query
Anatomy of a captured network packet

A trace of a packet's route

Serving requests
- Data centers
- Load balancing
- Application servers
- Databases
- Microservice architectures

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.





![]()



